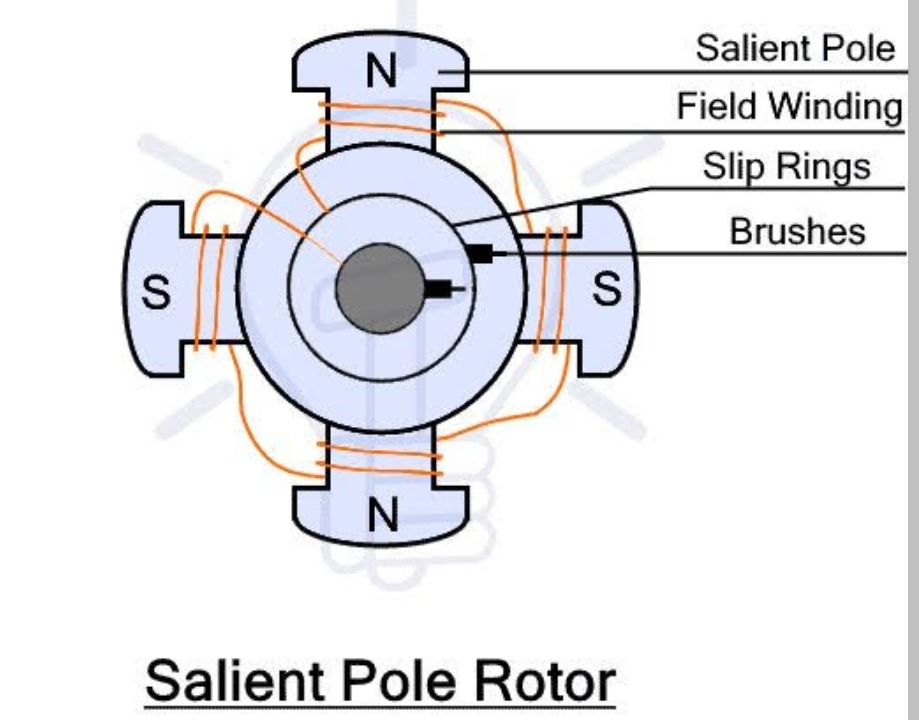
Salient Pole:
A salient pole is a type of magnetic pole used in electrical machines, particularly in synchronous motors and generators.
Applications:
- Synchronous Motors: Salient poles improve starting torque, efficiency, and power factor.
- Hydroelectric Generators: Salient poles reduce eddy current losses and increase efficiency.
- Wind Turbines: Salient poles optimize energy production and reduce maintenance.
- Electric Vehicles: Salient poles enhance motor performance, efficiency, and reliability.
- Power Systems: Salient poles stabilize grid frequency and voltage.
Advantages:
- High power density
- Improved efficiency
- Enhanced reliability
- Reduced maintenance
- Increased starting torque
Disadvantages:
- Complex design
- Higher cost
- Limited speed range
- Increased vibration
- Noise generation
Salient Pole Machines:
- Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines (PMSM)
- Electrically Excited Synchronous Machines (EESM)
- Hybrid Synchronous Machines (HSM)
Design Considerations:
- Pole shape and size
- Magnet material selection
- Winding configuration
- Cooling systems
- Mechanical stress analysis
Would you like:
- Detailed design guidelines
- Performance analysis
- Comparison with other magnetic pole types
- Application-specific solutions
- Research papers and case studies
Please respond!
Detailed Design Guidelines:
- Pole arc: 30-60 degrees
- Pole shoe shape: Rectangular or trapezoidal
- Magnet material: Neodymium (NdFeB), Samarium-Cobalt (SmCo)
- Winding configuration: Star or delta
- Cooling system: Air-cooled or liquid-cooled
Performance Analysis:
- Efficiency: 90-95%
- Power factor: 0.8-1.0
- Starting torque: 1.5-3 times rated torque
- Speed range: 100-3600 rpm
- Temperature rise: 80-120°C
Comparison with Other Magnetic Pole Types:
- Smooth poles: Lower efficiency, simpler design
- Inset poles: Higher efficiency, more complex design
- Buried poles: Higher reliability, lower starting torque
Application-Specific Solutions:
- Wind turbines: Direct-drive, high-torque salient pole motors
- Electric vehicles: High-efficiency, high-power salient pole motors
- Hydroelectric generators: Large-scale, high-efficiency salient pole generators
Research Papers and Case Studies:
- “Design and Analysis of Salient Pole Synchronous Motor” (IEEE)
- “Salient Pole Synchronous Generator for Wind Turbine Applications” (Elsevier)
- “Optimization of Salient Pole Motor Design for Electric Vehicle” (SAE)
Different features of Salient Pole machines:
Electrical Features:
- High power density
- High efficiency (90-95%)
- High power factor (0.8-1.0)
- Low stator current
- High starting torque
Mechanical Features:
- Robust construction
- Low vibration
- High reliability
- Compact design
- Easy maintenance
Magnetic Features:
- High magnetic flux density
- Low magnetic leakage
- High saliency ratio
- Optimized pole shoe design
- Reduced eddy current losses
Control Features:
- Vector control
- Direct torque control
- Field-oriented control
- Sensorless control
- Closed-loop control
Thermal Features:
- Air-cooled or liquid-cooled
- High thermal conductivity materials
- Optimized heat transfer design
- Reduced temperature rise
- Increased lifespan
Materials:
- Permanent magnets (NdFeB, SmCo)
- Electrical steel (Si-steel, Ni-Fe)
- Copper or aluminum windings
- Insulation materials (epoxy, polyester)
- Bearing materials (steel, ceramic)
Design Tools:
- Finite Element Method (FEM)
- Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
- Electrical circuit simulators (SPICE)
- Mechanical CAD software (SolidWorks)
- Optimization algorithms (genetic, particle swarm)
Applications:
- Wind turbines
- Electric vehicles
- Hydroelectric generators
- Industrial automation
- Aerospace and defense
Salient Pole (SP) vs Non-Salient Pole (NSP) machines
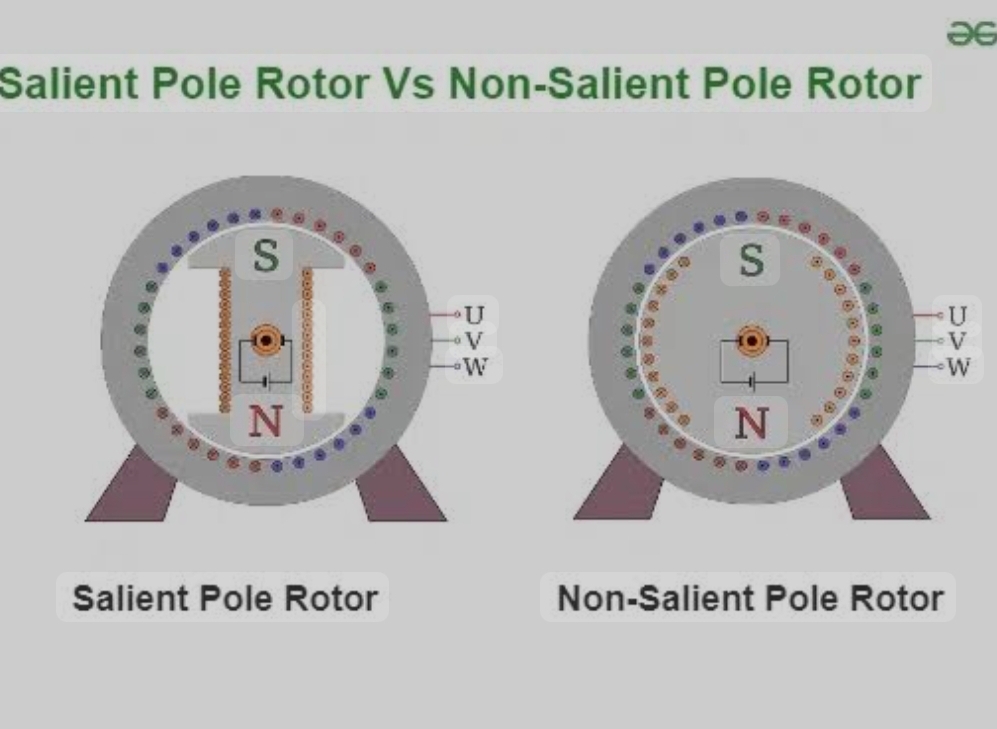
:
Salient Pole (SP) Machines:
Characteristics:
- Projection of poles from rotor surface
- Permanent magnets or electrical excitation
- High starting torque
- High efficiency
- High power density
Advantages:
- High power factor
- Low stator current
- High reliability
- Compact design
- Easy maintenance
Disadvantages:
- Complex design
- Higher cost
- Limited speed range
- Increased vibration
- Noise generation
Non-Salient Pole (NSP) Machines:
Characteristics:
- Smooth rotor surface
- No projections or permanent magnets
- Lower starting torque
- Lower efficiency
- Lower power density
Advantages:
- Simple design
- Lower cost
- Wide speed range
- Reduced vibration
- Quiet operation
Disadvantages:
- Lower power factor
- Higher stator current
- Lower reliability
- Larger size
- More complex control
Comparison:
| Feature | Salient Pole (SP) | Non-Salient Pole (NSP) |
|---|---|---|
| Starting Torque | High | Low |
| Efficiency | High | Low |
| Power Density | High | Low |
| Cost | High | Low |
| Complexity | High | Low |
| Speed Range | Limited | Wide |
| Vibration | High | Low |
| Noise | High | Low |
Applications:
Salient Pole:
- Wind turbines
- Electric vehicles
- Hydroelectric generators
- Industrial automation
Non-Salient Pole:
- Fans and blowers
- Pumps
- Conveyors
- General-purpose induction motors