What are the different special purpose of transformer?
You can use transformer as;
- Regulating transformers
- Converter transformer
- Rectifier transformer
- Mining transformer
- Welding transformer
What is reactor?
Reactors are equipment of transformer family. Reactors are used in the power system(network) for current limiting and for compensation of reactive power.
Types of reactors
- Series reactor: are necessary for limiting short-circuit currents, for limiting rush currents while switching-in for limiting current surges with fluctuating loads, for smoothing the current wavesform, etc.
- Shunt reactor: are necessary for shunt harmonic filter and for providing reactive power compensation for long AC lines.
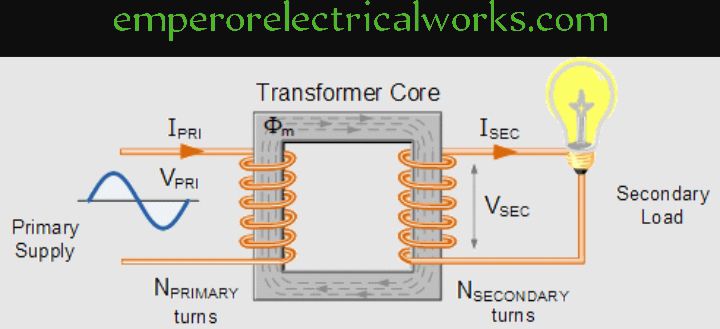
What is transformer?
Transformer is a static electrical equipment which transformer are electrical power from one voltage to another voltage at some frequency by electromagnetic induction. The transformer design, manufacturing and testing techniques have advanced with following objectives;
- High efficiency
- Low material cost, smaller size
- High reliability, long life, low maintenance.
- Low noise
- To conform to relevant specifications.
Important advances in power transformer technologies includes;
- Improved magnetic materials for core
- Lower losses
- Reduced size of core
2. Improved method of construction of core
- Elimination of core bolts
- Use of mired joint between laminations of leg and yoke.
3. Improved conductors and conductor insulators: multiple wire transposed conductors are now used, thereby the eddy current losses and skin effects are reduced.
4. Reduction in Noise: use of superior magnetic sheet steel, improved method construction of core and tank.
5. Improved design of windings and insulating system: The distribution of electrical stresses between winding and core, windings, turns of a winding, coils of a winding depends on electromagnetic phenomena,.
Types of transformer
- Core type transformer: A transformer on which the windings surrounded the limbs of the core.
- Shell type transformer: A transformer in which the core surrounds major portion of the windings.
Principle of operation of transformer
A transformer has two or more separate winding placed on a common magnetic core. It works on induction principle. The primary winding is supplied with alternating current of supply frequency. Thereby alternating magnetic flux of the same frequency is produced in the magnetic core.
What is testing in transformer?
Testing: is to ensure good health of transformer and trouble-free service
Kinds of test on a transformer
- Acceptance test: validates that your product is built and operating following design specifications and regulations. For transformers, it’s the process of testing to confirm that it meets all elements of the international standard
- Type test: type test prove the capabilities and guaranteed ratings
- Routine test: are conducted to verify that the manufactured and assembling are satisfactory
- Special test: are conducted in testing laboratory or at site to investigate certain phenomena.
- Site test: are carried out after complete installation to confirm that there are no transit damages and installation is satisfactory.
- Quality checks test: these are conducted on components, sub-assembling and complete assembly to confirm that the quality is satisfactory and there are no material/manufacturing defects.
What is a substation
A substation is an assemblage of electrical apparatus. Transformer are necessary in a sub-station for stepping-up and stepping-down of voltage. Besides transformers, substations has several other electrical equipment’s including bus-bars, circuit breaker, isolators, surge arrestors, etc.
- Busbars: Incoming and outgoing circuits connected to bus-bars.
- Circuit breakers: Automatic switching during normal or abnormal conditions.
- Insulators: Disconnection under no-load condition for safety, isolation and maintenance
- Earthing switch: To discharge the voltage on dead lines to earth.
- Current transformer: To step-down current for measurement, control and protection.